Home > Supported variables for integration mappings, shortcuts, and proactive chat
Categories: Integrations & Plugins
(Last Updated On: )
About This Article
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive overview of supported variables for use in integration mappings, shortcuts, and proactive chat.
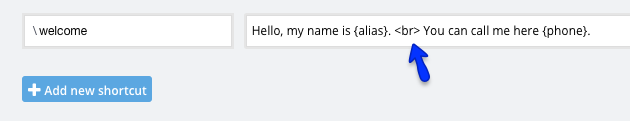
Shortcuts
Example:
{alias} for the agent alias
{phone} for the agent phone number
{js:xxx} for a JavaScript variable (where xxx is the name of the variable)
*You can use more than one variable if you add a break in the line. A <br> will do it for you.
Proactive Chat
Example:
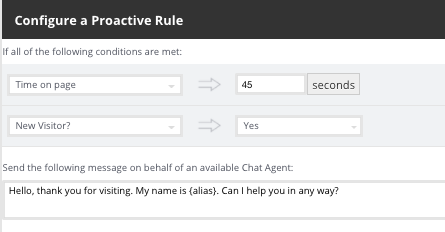
{alias} for the agent alias
{js:xxx} JavaScript variables. Read more here.
Integration mapping (custom mappings)
There are 4 source types.
- SnapEngage captured data
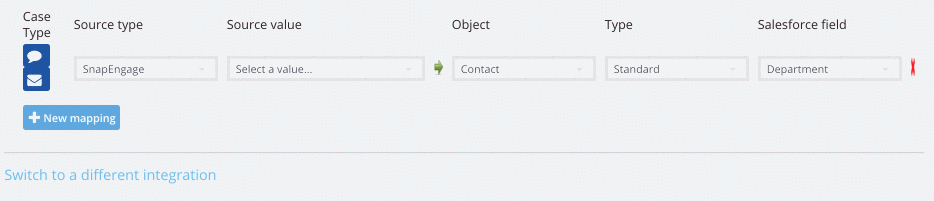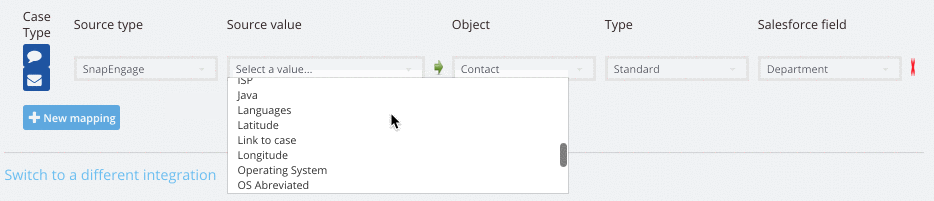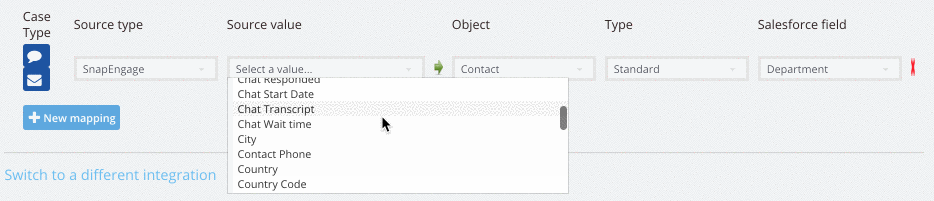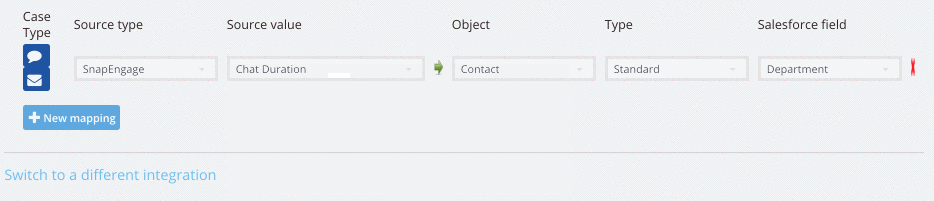
Browser = Which browser is the visitor using
Browser Abbreviated = Which browser is the visitor using minus version number
Browser Data (user agent) = Which browser the agent is using
Chat Agent Alias = The alias name for the agent configured with edit agent settings
Chat Agent IM ID = Chat agent email address
Chat Duration = The length of the chat
Chat End Date = Date the chat ended
Chat Ended By = Who ended the chat (agent, visitor, idled out)
Chat Responded = True or False was the chat responded to
Chat Start Date = The date the chat started
Chat Transcript = The transcript of the chat
Chat Wait Time = How long a visitor waited before an agent responded to the chat for the first time
City = The city from where the visitor chatted in from
Contact Phone = Visitors phone number (if available)
Country = The country from where the visitor chatted in from
Country Code = The code of the country from where the visitor chatted in from
Description = The visitors first message
Entry URL = This is the first page on your website where a visitor landed
Flash = Whether or not the visitor has Flash enabled. True or False
Full Geolocation = The full geolocation of the visitor
IP Address = The IP address for the visitor
ISP = The visitor’s Internet Service Provider{Java} =Whether or not the visitor has Java enabled. True or False
Languages = The visitor’s language
Latitude = The latitude of the visitor’s location
Link to case = A URL link for the transcript
Longitude = The longitude of the visitor’s location
Operating System = The operating system of the visitor
OS Abreviated =Abreviated info about the operating system of the visitor
Phonenumber = The visitor’s phone number if found during social discovery lookup.
Plugins = Any plugins the visitor has on their browser
Referrer Decoded = Displays the search term a visitor used to find your website. Only shows if visitor used a search engine to find you. (Only works with Bing as Google now encrypts searches)
Referrer URL = This is the URL from which a visitor arrived on your site. Also shown as “Coming from” on chat transcripts
Requester email = The visitor’s email address
Set Language Code = The language code (en,sp,fr, ect.)
Source Type = Will add following text “Message” for offline and Live_chat for online chats
State = The state from where the visitor chatted in from
Website (From) URL = The page the visitor started the chat on
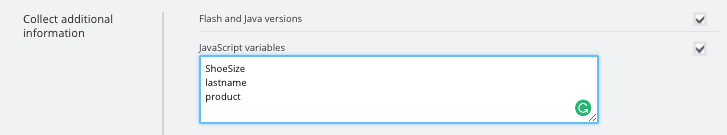
2. JavaScript. Here you can send over info captured by JavaScript variables from your pre-chat and offline forms. Variables must be added in the Collect additional information area (Settings > Options) first before you can see them in the custom mapping dropdown.
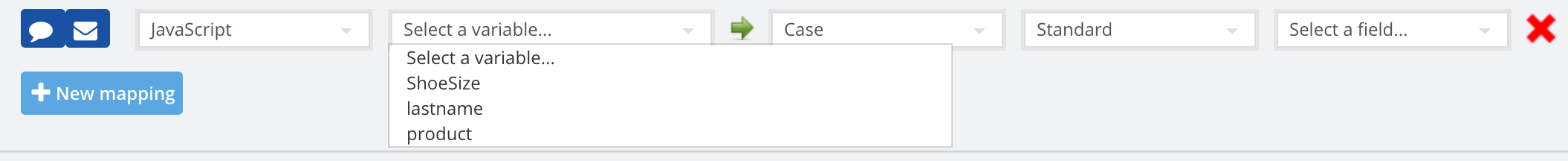
Refer to this doc to set this up
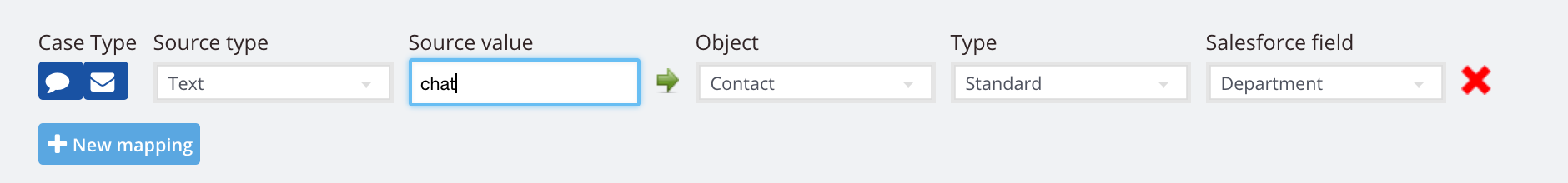
3. Text. Use this to send over text to a field of your choice.
4. Operator variables. Agents can capture during the chat, then you can send that info over to your field of choice.
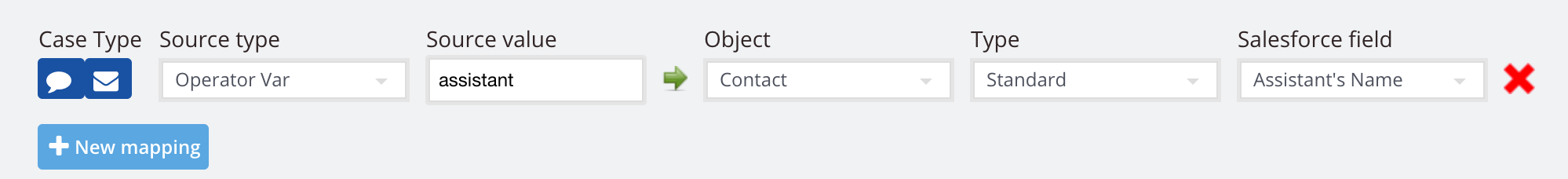
Refer to this doc to learn more about using operator variables.
Published February 15, 2013
Reader Feedback
No comments yet

 (2 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)
(2 votes, average: 4.50 out of 5)